Nail fungus is a generalized infection caused by opportunistic and pathogenic fungal infection with dermatophytes. About 20% of the adult population suffers from nail fungus and it is practically undetected in children.

reasons for infection
Fungi are widespread in the environment, but damage to human nails and skin develops only under favorable conditions. With age, the acidic pH of the skin can change to alkaline, which is favorable for fungal growth. Infection usually occurs by contact, if personal hygiene rules are not followed, the source of infection can be a sick person or objects in common use. Infection can occur in public places: swimming pools, saunas, gyms. And also in everyday life with the general use of slippers, socks, manicure accessories, towels and cloths.
The predisposing factors for onychomycosis infection are:
- decreased immunity;
- poor circulation in the legs, including when wearing tight shoes;
- excessive sweating;
- diabetes;
- obesity;
- mechanical nail injury;
- deformities and anatomical features of the feet.
Signs of nail fungus
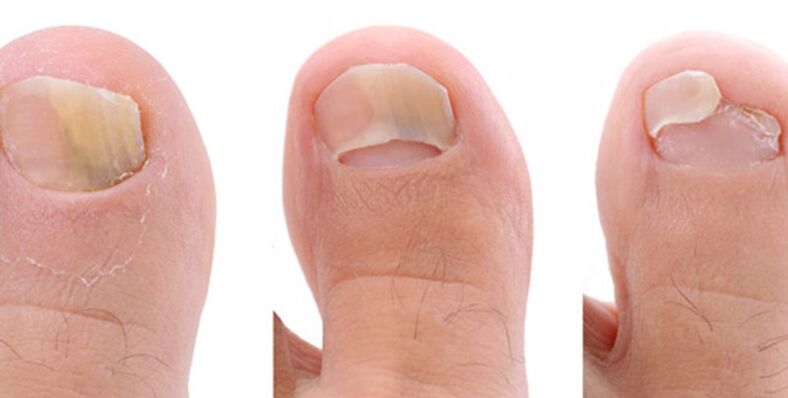
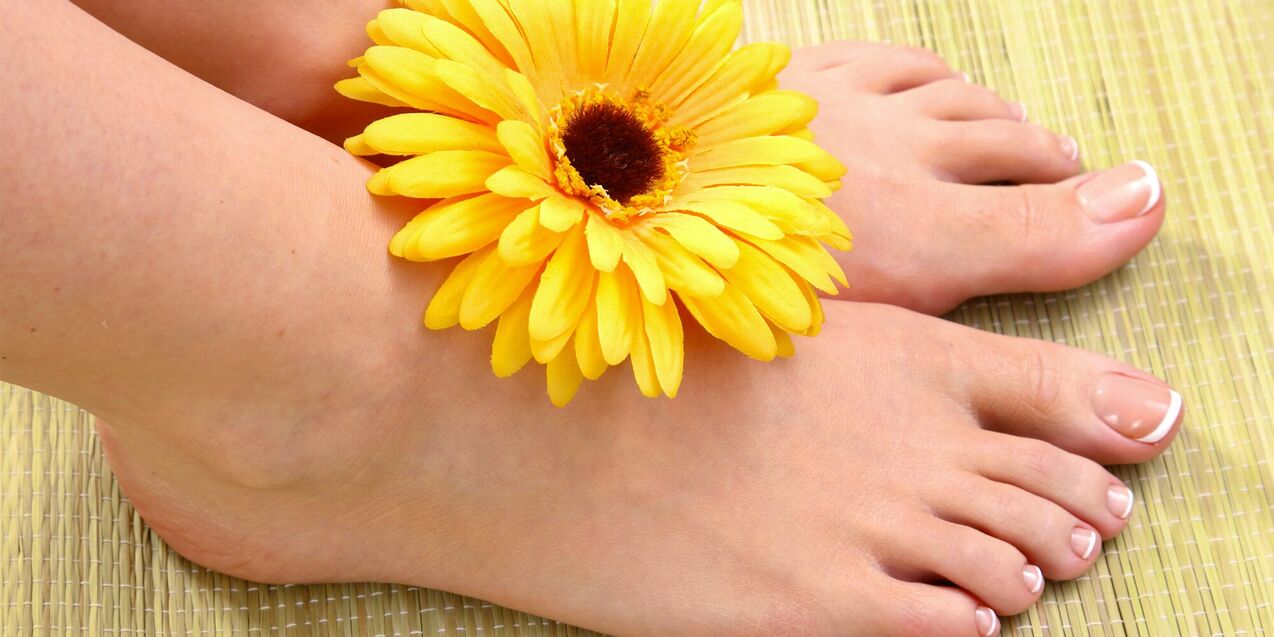
Nail fungus is a very persistent infection, the initial stage of the disease is expressed:
- discoloration of the nail plate, loss of shine;
- greater fragility;
- itching and irritation of the skin around the affected nail;
- pain at the injury site, especially when wearing tight shoes;
- highlighting part of the nail from the nail bed.
As the progression and involvement of the entire nail plate in the process, new symptoms appear: the nail thickens and deforms significantly.
Depending on the degree of nail damage, three types of onychomycosis are distinguished:
- Normotrophic - manifested by a distortion of the nail color from white to dark green. The color initially changes in spots or stripes and gradually covers the entire surface of the nail, while the thickness of the nail plate does not change and the shine remains.
- Hypertrophic - is expressed by discoloration, loss of luster and severe thickening and deformation of the nail. The nail is heavily exfoliated and partially destroyed;
- Atrophic - reflected by discoloration, thinning and subsequent rejection of the affected area.
Which doctor treats the fungus?
You can determine the infection yourself, but only a doctor can confirm the diagnosis. If you find a change in nail color, increased brittleness, you should consult a dermatologist. The doctor prescribes a microscopic diagnosis or cultural study to confirm the diagnosis. A part of the affected nail is removed for analysis or nearby tissues are scraped off. Timely detection of nail fungus greatly facilitates treatment and prevents the development of complications. Released onychomycosis is dangerous as it can cause mycotic eczema, aspergillosis, decreased immunity, infection of all nails, skin and other organs.
nail fungus treatment

How to treat onychomycosis is determined by the doctor depending on the degree of nail plate alteration, clinical form, degree of hyperkeratosis and length of the affected area. For treatment, local agents (ointments, drops, sprays, varnishes) and general agents (antimycotic drugs) are used.
As a rule, with minor changes to the nail, drugs are used for topical treatment. Before treatment with antifungal solutions, ointments, varnishes, the affected area of the nail must be surgically removed or with the help of keratolytic drugs. This is necessary for better penetration of the antifungal drug deep into the damaged tissues, which allows you to get rid of the fungus much faster.
Keratolytic drugs contribute to the softening of the nail and its easy and painless removal, produced in the form of plasters, which include urea or salicylic acid:
- ureaplast;
- quinosol urea plaster;
- quinosol-salicylic adhesive;
- onychoplast;
- quinosol-dimexide patch;
- mycospores (combined preparation).
Before gluing the plaster, it is necessary to scrape the top layer of the nail, apply a therapeutic mass and glue it with a tape, change the dressing every 1-2 days. Before the change, the affected areas of the nail are removed with scissors and antifungal agents are applied.
Antifungal creams, ointments and drops are:
- ketoconazole-based;
- clotrimazole derivatives;
- micanazol-based;
- oxycanazol derivatives;
- terbinafine-based;
- chloronitrophenol derivatives;
- based on naftifine.
Ointments, creams and drops should preferably be applied to the open nail bed 2-3 times a day, until the final restoration of the nail. These drugs are active against the vast majority of pathogens, but they are not capable of penetrating the entire depth of the nail plate.
Local antiseptics - a solution of iodine, dyes, quinosol, organic acids are often used in the treatment of nail fungus, if it is impossible to use other means. The main advantage, the antiseptic is cheap and widely available. Local antiseptics, such as iodine, treat the affected nail up to three times a day for a month. When applying the solution, it is advisable not to touch the surrounding skin to avoid burns. A burning and tingling sensation helps to recognize the onset of exposure.
If local treatment is ineffective, antifungal tablets are also prescribed, prescribed by a specialist.
Correctly selected combination therapy helps to cure advanced onychomycosis faster. In addition, treatment combined with local and general therapy is prescribed for more than three affected nails, for people over 50 years old and with slow nail growth. The use of combination therapy can significantly reduce the duration of treatment.
Fungal treatment with folk remedies

For the preparation of antifungal agents at home, you can use - apple cider vinegar and herbal preparations:
- mix in equal parts vegetable oil and apple cider vinegar, moisten a cotton pad in the resulting solution and apply to the affected nail for 4 hours, for convenience, you can fix the bandage with a tape. The procedure is performed daily for a month;
- for the treatment of a neglected process, a mixture of 9% vinegar with celandine helps, the resulting composition must be infused for a month. Then add 50 g of salt. The resulting product is used for foot baths for 5 to 10 minutes before bed. It is important not to clean your feet after bathing, but to let them dry on their own;
- to treat the affected nail, you can use an alcoholic solution of propolis, juice or porridge of onions, garlic. A blend of lavender and tea tree oils also works well;
- herbal decoction for foot baths: mix in equal proportions oak bark, calendula, horsetail, verbena. Pour 50 g of the resulting mixture with boiling water and keep in a water bath for about 15 minutes.
Prophylaxis
Damage caused by nail fungus can be easily avoided with good personal hygiene:
- It is necessary to wash the feet daily with antiseptic agents.
- Dry your feet with a personal towel.
- Use a pumice stone to remove old skin, which is a good growth medium for fungus.
- Use medications that reduce foot sweating.
- Change socks, knee socks and tights daily.
- Wear loose, comfortable shoes. Do not wear wet shoes.
- Wear shoes when visiting pools and showers.
- Do not wear other people's shoes, slippers, socks, towels, manicure accessories.
- Use pharmacological preparations for protection before visiting beaches, swimming pools, saunas.